I learnt
about a very interesting topic, which is topology. What is topology
actually? Network (LAN) topology is actually the study of the arrangement or
mapping of the elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a network, especially the
physical (real) and logical (virtual) interconnections between nodes. Network
topology is divided into two types, which are the physical topology and also logical
topology.
1. Physical topology is
the physical layout of devices on a network or the way that the devices on a
network are arranged and how they communicate with each other
- The
way that the workstations are connected to the network through the actual
cables that transmit data - the physical structure of the network
- the
way that the signals act on the network media, or the way that the data passes
through the network from one device to the next without regard to the physical
interconnection of the devices.
Types/Classification
of physical topologies:
a.
Linear Bus
b.
Star
c.
Star-Wired Ring
d.
Tree
e.
FDDI
f. Mesh
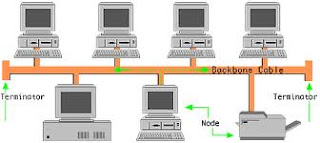
- Linear bus
- A
linear bus topology consists of a main run of cable with a terminator at each
end.
- All
nodes (file server, workstations, and peripherals) are connected to the linear
cable.
- Ethernet
and LocalTalk networks use a linear bus topology.
- The
bus cable carries the transmitted message along the cable. As the message
arrives at each workstation, the workstation computer checks the destination
address contained in the message to see if it matches its own. If the address
does not match, the workstation does nothing more.
- If
the workstation addresses matches that contained in the message, the
workstation processes the message. The message is transmitted along the cable
and is visible to all computers connected to that cable.
-
neighbor forming a ring.
-
The main difference between the bus and ring is that the ring topology does not
require termination. Because the systems are connected all together in a loop,
there is no beginning and end point as there is with the bus topology.
-
This configuration is seen in Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) networks.

No comments:
Post a Comment